Benefits of Fiber Over Copper
Jul 19, 2021 | Home Technology
One question we are often asked is, “Why fiber?” It’s a fair question. Why does it matter how the internet gets to your home, so long as it does? But if you’ve ever experienced a slow internet connection, you know it matters. The type of cabling carrying the internet directly affects how fast it gets to you, which affects your online experience.
In the early days of the internet, most surfing was done over copper cables for two main reasons. First, thanks to telephones, copper cables were already in the ground and on utility poles. Second, internet connectivity didn’t need to be fast because we used 56.6-baud dialup modems (think screeching sound when logging on) and mostly sent text-based emails to one another. But as the demand for large image files and then video files rose, internet speed needed to increase to keep up. Add streaming services and video calls into the mix and today’s internet needs are higher than ever. Copper couldn’t keep up. It simply wasn’t fast enough.
Enter fiber optics, stage right. Invented in 1970 by glass manufacturing giant Corning, Inc. at their research headquarters in Corning, NY, the tiny fiber optic strands quickly proved an unequaled ability to carry vast amounts of data over long distances at ultra-high speeds. Over the next 51 years, fiber optic technology advanced even further with the invention of many varieties of specialty fibers. Today, fiber optics are the preferred means of carrying enormous amounts of data over both long and short distances. But how does fiber perform so well? It all starts with capacity.
Faster
If you’ve been around the internet very long, you’ve probably heard the term “bandwidth” thrown about. Bandwidth is how much data a cable can transmit at any given time. More is better because more is faster. For example, copper can transfer up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps). Sounds impressive, right? That is until you realize fiber optics can transmit up to 60 Terabits per second, the equivalent of over 7,000 Gbps – over 700 times faster than copper. As a result, games, files, and streaming video run smoother and faster on fiber.
Farther

One challenge of transmitting data is getting it from point A to point B, especially when point A and point B are miles apart. This is especially difficult for copper cables because they can only transmit data signals up to 100 meters – basically a football field length – without a boost. That’s not very far. Conversely, fiber optic cables can transmit data up to 25 miles unassisted. And over those 25 miles, the fiber experiences only about 3% signal loss (called “attenuation”) vs. close to 90% signal loss over the same distance for copper, even with boosts along the way. All of this means better data integrity across longer distances with fiber.
Clearer
One common challenge with copper cable is how to protect it against electronic interference or electronic noise. This interference can be caused by radio signals, other nearby copper cables, and electrical wires. The resulting interference can cause signal distortion and loss, lowering the data quality and, therefore, the user experience. On the other hand, fiber does not experience this interference because it uses pulses of light, called packets, to send interference-free signals down the cable, ensuring a better user experience.
More Durable
As odd as it may sound, fiber is more durable than copper. How can that be? Despite being significantly smaller than copper and made from glass, fiber strands are tougher and more rugged than copper, less prone to breakage during installation and after. This results in a longer-lasting connection between point A and point B than with copper cabling. Fiber cables are also less susceptible to damage from weather, such as extreme cold or extreme heat. This means they can be buried in the ground or strung from poles in all sorts of climates, from the hottest jungle to the coldest arctic regions, and work fine.
Better Security
In the old days, when copper was king, tapping into a cable was easy. Just reroute the line through the eavesdropping device and nobody was the wiser. Unfortunately, legacy copper cabling can still be a problem today, with bites and bits moving from computer to server and back, just as vulnerable as before.

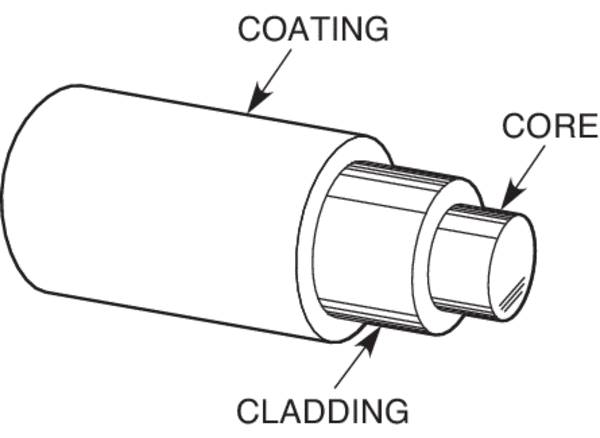
With fiber, however, tapping or breaking into a cable undetected is nearly impossible, thanks to more sophisticated electronics on both ends of the fiber constantly monitoring potential breaks or hacks. If a tap is inserted into a fiber cable, the temporary interruption, no matter how short, can be detected immediately, preserving valuable data. Non-tap hacks, such as external listening devices designed to pick up signals that leak from copper cables, won’t work on fiber because the signal never leaves the cable, held in by the fiber’s cladding and coating, leaving the outside listening device with nothing to hear.
Infinite Scalability
Copper cabling is nearing the end of its internet life cycle, with bandwidth requirements far exceeding its ability to handle the growing data traffic needs. It is still a viable and reliable source of electricity, primarily because fiber can’t provide its own power. However, fiber optic cable is far from full, with plenty of room for growth. In addition, fiber is much better equipped to handle the ever-increasing demands on internet connectivity. As demand increases, fiber is there to accommodate it.
Overall Better Experience
Whether you need to transmit large amounts of important information quickly or want to hang out on the couch tonight and watch your favorite streaming service, fiber optics is the best way to be sure your internet can handle it all.
- fiber vs copper
- Fiber internet
- high speed internet
- home internet
- business internet