Demystifying Common Internet Tech Terms
Aug 8, 2023 | Home Technology, Helpful Tips
A Beginner's Guide to Navigating the Digital World
The internet has become an integral part of our daily lives, connecting us to a vast world of information and possibilities. However, understanding the jargon and technical terms associated with internet technology can often be confusing. Let's look at some of the most common internet tech terms in plain language to help you navigate the digital landscape with ease.

Upload and Download
Upload and download refer to the two directions data flows through your internet connection. When you send an email, post photos or videos to social media, or back up your files to the cloud, you are uploading data. It's going from your device up to the web.
On the other hand, when you browse the web, stream videos, or download files, you are engaging in download activities because that data is coming to you from a server located elsewhere.
Traditional internet providers such as DSL and cable can only provide asymmetrical or lopsided upload and download speeds, where uploading is significantly slower than downloading. Fiber internet, on the other hand, offers symmetrical upload and download speeds so data flows in both directions at the same speed.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection in a given time. It is usually measured in Mbps or Gbps.
A higher bandwidth allows for faster data transfer, meaning you can load websites, download files, and stream media more quickly.
Mbps and Gbps
Mbps stands for "megabits per second," and Gbps stands for "gigabits per second." Both are units used to measure the speed at which data travels through your internet connection. A Gigabit is 1,000 Megabits.
Think of it like water flowing through a pipe: Mbps and Gbps indicate how fast the data is flowing to and from your devices. Higher Mbps or Gbps values mean faster internet speeds, allowing you to browse the web, stream videos, and download files more quickly.
Wi-Fi
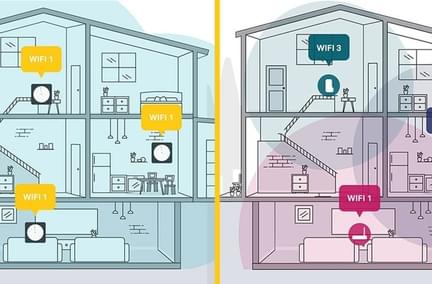
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that allows devices like smartphones, laptops, and smart devices to connect to the internet without using physical cables. It works by transmitting data over radio waves, enabling you to access the internet from different parts of your home or public spaces with Wi-Fi hotspots.
Wi-Fi performance depends not only on the speed of the internet coming into the home but also on the type of Wi-Fi network and the Wi-Fi network's layout.
Smart Devices
Smart devices, also known as IoT, are everyday objects that can connect to the internet and communicate with each other. Examples include smart speakers, smart thermostats, smart lights, and smart appliances.
These devices often offer enhanced functionality and convenience, as they can be controlled remotely through smartphone apps or voice commands.
How fast these devices operate depends on two factors: the speed of the internet coming to the home and the technology inside each device. Is the device capable of handling the speeds your internet service provides?
Router
A router is a crucial device that acts as a traffic director for data flowing between your devices and the internet. It connects to your modem and allows multiple devices to access the internet simultaneously through a local network. The router also helps ensure that data packets reach their intended destinations efficiently.
Modem
A modem, short for "modulator-demodulator," is another critical piece of equipment required to connect to the internet. It converts digital data from your devices into analog signals that can travel over traditional telephone lines or cable systems. Conversely, the modem translates incoming analog signals back into digital data that your devices can understand.
Latency
Latency is the time delay between when data is sent from your device to a server and when the server responds. It is measured in milliseconds (ms). Low latency is crucial for activities like online gaming, where even a slight delay can affect your performance.
Ping
Ping is a term commonly used to measure the latency between your device and a server on the internet. It is expressed in milliseconds (ms). A lower ping value indicates a quicker response time, which is essential for online gaming, video conferencing, and other real-time applications.
Jitter
Jitter refers to the variation in latency over time. In other words, it measures how consistent your internet connection's response time is. A stable and consistent connection will have low jitter, whereas high jitter can lead to disruptions in video and voice calls.
VoIP
VoIP stands for "Voice over Internet Protocol." It is a technology that enables you to make voice calls over the internet rather than using traditional telephone lines. VoIP services like Skype, Zoom, and WhatsApp allow people to communicate with each other using voice or video calls, often at lower costs than traditional phone services.
It can also be the connection for a landline if you have fiber internet. For example, landline phone service from Gateway Fiber works on VoIP, placing and receiving calls on the same fiber network that powers the high-speed internet.
Now that you know...
Understanding these common internet tech terms can empower you to make informed decisions about your internet service, devices, and online activities.
Whether you're choosing an internet plan, troubleshooting connection issues, or exploring new smart devices, this knowledge will help you navigate the digital world with confidence. Embrace the possibilities that the internet offers, and let your newfound understanding of tech terms be your guide to a more connected future.
- common internet tech terms
- Mbps
- Gbps
- modem
- router
- voip
- Wi-Fi
- smart devices
- IoT
- download speed
- upload speed
Related Articles
Aug 8, 2023